Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
What type of point mutation causes translation to be terminated prematurely, resulting in a shorter polypeptide than was encoded by the normal gene?
Nonsense mutation | |
Missense mutation | |
Frameshift mutation | |
Deletion |
Question 1 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Typically substitutions result in missense mutations, and the altered codon still codes for an amino acid. But if a point mutation changes a codon for an amino acid to a stop codon, it is called a nonsense mutation.
Question 2 |
This type of mutation frequently alters the genetic message by changing the reading frame, causing all the nucleotides “downstream” of the mutation to be improperly grouped into codons.
Mutagen | |
Base-pair substitution | |
Nonsense mutation | |
Frameshift mutation |
Question 2 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). If a nucleotide is inserted or deleted in a gene, it will change the reading frame of the genetic message. The triplet grouping of bases on the mRNA that is read during translation will be altered, along with every grouping after the insertion or deletion. The result is typically extensive missense.
Question 3 |
Questions 3–4
In the classic experiment by Frederick Griffith, two strains of the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae were studied. The smooth “S” strain bacteria can cause pneumonia in mice because they have a capsule that protects them from the defense system of animals. The rough “R” strain bacteria do not have a capsule, and are thus nonpathogenic. Griffith injected the mice with two strains of the
bacteria to test for the trait of pathogenicity.
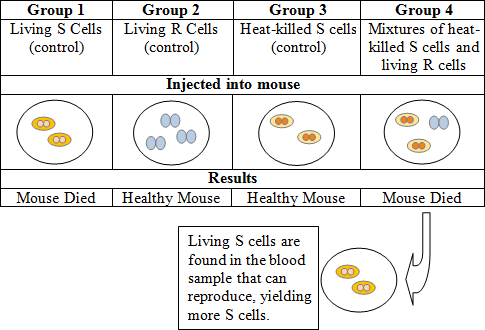

What important conclusion did Griffith reach after conducting his experiment?
Killing bacteria cells with heat is not an effective way to cure pneumonia | |
Heat-killed S cells regenerate themselves inside of organisms | |
It is impossible to kill Streptococcus pneumonia | |
Living R bacteria had been changed into pathogenic S bacteria by an unknown substance |
Question 3 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Griffith was attempting to develop a vaccine against pneumonia when he discovered the process of transformation, which is a change in genotype and phenotype due to the assimilation of external DNA by a cell.
Question 4 |
Questions 3–4
In the classic experiment by Frederick Griffith, two strains of the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae were studied. The smooth “S” strain bacteria can cause pneumonia in mice because they have a capsule that protects them from the defense system of animals. The rough “R” strain bacteria do not have a capsule, and are thus nonpathogenic. Griffith injected the mice with two strains of the
bacteria to test for the trait of pathogenicity.


Which group demonstrates that DNA is the agent of transformation?
Group 1 | |
Group 2 | |
Group 3 | |
Group 4 |
Question 4 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Since it was found that the S cells were able to reproduce, the agent of transformation must be DNA.
Question 5 |
Which type of bacteriophage reproduces only by the lytic cycle?
Virulent phage | |
Temperate phage | |
Prophage | |
Lysogenic phage |
Question 5 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The lytic cycle is the type of phage reproductive cycle that results in the death of the host cell. The bacterium breaks open (lyses) and releases the phages that were produced within the cell.
Question 6 |
What enzyme is responsible for the reverse information flow of RNA to DNA in retroviruses, such as HIV, allowing the virus’s genetic information to be permanently integrated into the hosts cell’s DNA?
DNA polymerase | |
RNA polymerase | |
Reverse transcriptase | |
Telomerase |
Question 6 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Reverse transcriptase catalyzes the formation of a strand of DNA from an RNA template.
Question 7 |
Bacteriophages are able to carry bacterial genes from one host cell to another resulting in genetic recombination. This process is called:
Conjugation | |
Transformation | |
Transduction | |
Mutation |
Question 7 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Transduction occurs when bacteriophages carry bacterial genes form one host cell to another. This usually results from an accident during the phage reproductive cycle. The virus that carries the DNA may not be able to reproduce because it lacks its own genetic information. The virus may be able to attach to another bacterial cell and inject the bacterial DNA into the next cell. If this DNA replaces the homologous region of the recipient cell’s chromosomes by DNA recombination, then it has introduced genetic variation into the subsequent cell.
Question 8 |
During metaphase I of meiosis I, homologous pairs of chromosomes are situated along the metaphase plate. The orientation of each pair is random, resulting in a 50% chance that a particular daughter cell will get the maternal chromosome and a 50% that the daughter cell will get the parental chromosome. This is one aspect of sexual reproduction that contributes to genetic variation, and is called:
Independent assortment | |
Separation of homologs | |
Cytokinesis | |
Reductional division |
Question 8 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Since each homologous pair of chromosomes is positioned independently of the other pairs, the division at the end of meiosis I results in each pair sorting its maternal and parental homologs into daughter cells independently.
Question 9 |
During prophase I of meiosis, a reciprocal exchange of genetic material between nonsister chromatids producing chromosomes with new combinations of material and parental alleles. This is called:
Synapsis | |
Crossing over | |
Codominance | |
Reductional division |
Question 9 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Crossing over begins in prophase I when homologus pairs of chromosomes pair loosely along their lengths. The genes on each homolog are precisely aligned with the corresponding gene on the other homolog. Proteins facilitate the swaping of corresponding segments of two nonsister chromatids to result in new combinations of maternal and parental alleles.
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 9 questions to complete.
|
List |
Next Practice Test:
Cell Communication >>
AP Biology Main Menu >>
