Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
In a typical human cell, only about 20% of the genes it contains are expressed (even less in muscle and nerve cells), even though almost all the cells in the organism contain the same DNA. The set of genes expressed in each cell is unique, which allows the cells to perform different functions.
This expression of different genes by cells within the same genome is known as:
Positive gene regulation | |
Negative gene regulation | |
Differential gene expression | |
Genomic imprinting |
Question 1 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Positive and negative gene regulation are used by bacteria to respond to environmental change. Genomic imprinting takes place when the expression of an allele is determined by which parent the gene was inherited from.
Question 2 |
If a mutation causes a misplacement of a structure on an organism, such as a leg growing where an antennae on a fruit fly should be, the mutation is likely to be in:
A homeotic genes | |
ras genes | |
p53 genes | |
Maternal effect genes |
Question 2 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Homeotic genes control the development of the overall organization of the body.
Question 3 |
If a mutation in a cell inhibits the production of a tumor-suppressor protein, the cell is much more likely to:
Develop cancer | |
Enter homeostasis | |
Enter apoptosis | |
Become an embryonic lethal |
Question 3 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Cells contain genes that inhibit cell division, called tumor-suppressor genes, which help to prevent uncontrolled cell growth, or cancer.
Question 4 |
Which statement best describes when the role of the tryptophan operon when adequate tryptophan is present in the cell?
The repressor is inactive and the operon is turned “off,” haulting the production of tryptophan | |
Tryptophan acts as a corepressor and activates the repressor, stopping the production of tryptophan | |
The repressor becomes active, the operon is turned “on” and tryptophan is produced | |
Tryptophan is present, the repressor is active, and the operon is turned “on” |
Question 4 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The tryptophan operon is a repressible operon. When there is enough tryptophan in the cell, tryptophan acts as a corepressor and activates the repressor, changing its shape. The activated receptor binds to the operator and prevents the RNA polymerase from binding to the repressor and stops transcription. The tryptophan operon is a repressible operon, and therefore it is always switched on unless the repressor is activated.
Question 5 |
Mad cow disease causes normal versions of a protein in the brain to misfold, causing brain damage. What is responsible for the change in the shape of the protein?
Repressor genes | |
RNA polymerase | |
Prions | |
The tryptophan operon |
Question 5 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Prions are misfolded versions of a protein which are infectious and cause brain diseases. Prion diseases occur when prion protein becomes abnormal and clump in the brain, When the prions accumulate in the brain it can cause memory impairment, personality changes, and difficulties with movement. Prion diseases are fatal.
Question 6 |
Which statement best describes the function promoter?
An enzyme that transcribes a new RNA chain by linking ribonucleotides to nucleotides on a DNA template. | |
A protein that prohibits gene transcription. | |
A nucleotide sequence in DNA that is the binding site of RNA polymerase, positioning the RNA polymerase to begin transcription at the appropriate position. | |
A sequence of nucleotides near the start of an operon where the active repressor can attach. |
Question 6 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). A promoter is a nucleotide sequence in DNA that is the binding site of RNA polymerase, positioning the RNA polymerase to begin transcription at the appropriate position.
Question 7 |
During this stage of gene expression, genetic information is copied from the template strand of DNA.
RNA Processing | |
Translation | |
Replication | |
Transcription
|
Question 7 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Pre-messenger RNA carries information from DNA by copying the genetic information through a process called transcription.
Question 8 |
During this stage of gene expression, mRNA is processed through ribosomes and polypeptides are linked together into chains.
RNA Processing | |
Translation | |
Replication | |
Transcription
|
Question 8 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Molecules of mRNA are processed through ribosomes and codons are translated into amino acids. tRNA molecules translate the codons on the mRNA molecules, and deliver amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain.
Question 9 |
This process involves modifying the ends of the pre-mRNA molecules by modifying each end, cutting out introns and splicing remaining parts together.
RNA Processing | |
Translation | |
Replication | |
Transcription |
Question 9 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Enzymes change the ends of the pre-mRNA molecule by adding a 5' cap to the 5' end. The 3' end is modified by adding a poly-A tail. Also, during this stage, introns (non-coding segments of a nucleic acid) are removed and the remaining mRNA exons are joined back together.
Question 10 |
Which answer shows the correct sequence of information flow from gene to protein?
Transcription → Translation → RNA Processing
| |
RNA Processing → Translation → Transcription
| |
Transcription → RNA Processing → Translation
| |
Translation → RNA Processing → Transcription |
Question 10 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Genetic information is transcribed onto a pre-mRNA molecule, then it is modified during RNA processing, and finally it is used to make polypeptides in translation.
Question 11 |
If a DNA template strand has the following sequence, what is the correct mRNA sequence?
DNA Template Strand Sequence: AAACCGAGTTTTGGCTCA | |
AAACCGAGT | |
UUUGGCUCA | |
GGGTTUGUA |
Question 11 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). mRNA’s pairs with DNA with the following base pairs: A – U and C – G.
Question 12 |
Questions 12–13
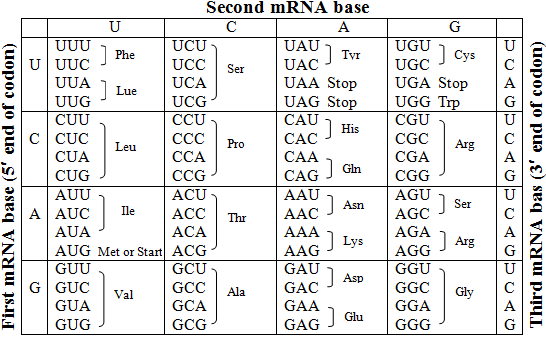
If a codon has the following sequence, what is the anticodon?
Codon: UCATCA | |
AGT | |
UCA | |
AGU |
Question 12 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). mRNA base’s complementary base pairs are A – U and C – G.
Question 13 |
Questions 12–13

If a DNA template strand’s DNA sequence is AAA, what amino acid will be formed?
Lys | |
Phe | |
Pro | |
Gly |
Question 13 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). A triplet code of AAA on a DNA strand is translated into the codon UUU. Using the chart, UUU codes for the amino acid Phe.
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 13 questions to complete.
|
List |
Next Practice Test:
Genetic Variation >>
AP Biology Main Menu >>
