Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
Which of the following molecules is a carbohydrate?
Palmitic acid | |
Collagen | |
Insulin | |
Lactose |
Question 1 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Anything that ends in the suffix –ose is a sugar and sugars are carbohydrates.
Question 2 |
Use the diagram below to answer questions 2–3.
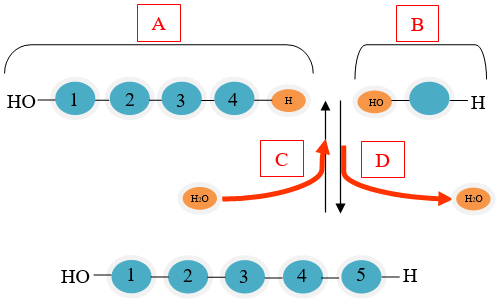
Which part of the diagram is showing a monomer?
A | |
B | |
C | |
D |
Question 2 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Monomers are small units that are joined together to form polymers.
Question 3 |
Use the diagram below to answer questions 2–3.

Which part of the diagram shows a condensation reaction?
A | |
B | |
C | |
D |
Question 3 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Condensation reactions occur when monomers are connected by the removal of a water molecule.
Question 4 |
There are four levels of protein structure. Which level includes the coils of the α helix and the folds of the β pleated sheets?
Primary structure | |
Secondary structure | |
Tertiary structure | |
Quaternary structure |
Question 4 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Primary structure refers to the sequence of amino acids. Secondary structure includes the α helix and the β pleated sheets. Tertiary structure is the overall shape of the protein. Quaternary structure consists of two or more polypeptide chains aggregated into a functional macromolecule.
Question 5 |
Which of the following statements correctly describes the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats?
Saturated fats tend to be solid at room temperature; unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature | |
Saturated fats are cannot pack together closely because of their bent structure; unsaturated fats can pack together because they are flat | |
Saturated fats come from plants and fish; unsaturated fats are from animals (except fish) | |
Saturated fats are considered “healthy” fats; unsaturated fats may contribute to cardiovascular disease |
Question 5 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Saturated fats tend to be solid at room temperature and are mostly obtained from animal, not plant, sources. Unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature and are primarily obtained from plants and fish sources. Healthful diets tend to be higher in unsaturated fats and lower in saturated fats.
Question 6 |
Which of the following nucleic acids is not found in RNA?
Cytosine | |
Thymine | |
Adenine | |
Guanine |
Question 6 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). In RNA, thymine (nucleic acid present in DNA) is replaced with uracil.
Question 7 |
Which group of organelles works together to regulate protein traffic and performs metabolic functions of the cell?
Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, and vacuoles | |
Nucleus and ribosomes | |
Mitochondria, chloroplast, peroxisome | |
Nuclear envelope, nucleolus, chromatin |
Question 7 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The eukaryotic cell’s genetic functions are housed in the nucleus and carried out by the ribosomes. The mitochondria and chloroplasts change energy from one form to another. The nuclear envelope, nucleolus and chromatin are all part of the nucleus.
Question 8 |
Although animal cells lack cell walls, they have a complex network of glycoproteins that provide structure and strength to the cell, referred to as:
Desmosomes | |
Extracellular matrix | |
Intermediate filaments | |
Cytoskeleton |
Question 8 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Desmosomes are intercellular junctions that function like rivets. Intermediate filaments are a group of cytoskeletal elements. The cytoskeleton refers to the fibers that organize activities and structures inside the cell.
Question 9 |
Which group of cellular structures form the endomembrane system?
Microtubules, microfilaments and intermediate filaments | |
Endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vesicles | |
Mitochondria and chloroplasts | |
Fimbriae, nucleoid, flagella |
Question 9 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Microtubules, microfilaments and intermediate filaments are parts of the cytoskeleton structure. The endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vesicles form the endomembrane system. The mitochondria and chloroplasts change energy from one form to another. Fimbriae, nucleoid and flagella are components of a prokaryotic cell.
Question 10 |
If you were late to biology class, and the instructor was discussing hyphae, chitin and mycelium, what could you assume was the topic for the day’s discussion?
Protists | |
Prokaryotic cells | |
Fungi | |
Insects |
Question 10 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Hyphae (filaments forming the body of fungi), chitin (found in fungal cell walls) and mycelium (feeding network fungi) are all parts of fungi.
Question 11 |
A study conducted on bumblebees in Colorado showed how different species of Bombus complete for nectar. Different species appeared to have adaptations that allowed them to exploit different species of plants based on the corolla length of the plant’s flowers. Different bumblebee species preferred different corollas in accordance with the length of their proboscis. In other words, bee species with a long proboscis preferred flowers with a long corolla, and bee species with a short proboscis preferred flowers with a short corolla.
This is an example of:
Resource partitioning | |
Competitive exclusion | |
Character displacement | |
Relative abundance |
Question 11 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Resource partitioning allows similar species to coexist by using different sets of resources.
Question 12 |
Late in the 19th century, hundreds of wolves roamed the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem. The wolves were eradicated because it was feared that they would devastate the abundant herds of elk and bison, as well as local livestock. The removal of the wolves from the ecosystem caused a cascade of events that changed the entire Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem. First, the elk populations exploded, which led to greater competition between elk herds competing for food. Their overgrazing reduced the size of populations of other species which rely on the plants for survival, such as fish, beaver and songbirds. Additionally, stream banks eroded as a result of the overgrazing, allowing soil and sediments to enter the water. Realizing their mistake, the US government began reintroducing wolves to the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem, and many of these problems have begun to reverse.
The importance of the wolf species in the ecosystem has led conservation biologists to consider the wolves to be a(n):
Invasive species | |
Foundation species | |
Keystone species | |
Mutualistic species |
Question 12 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Keystones species are those that exert such a strong control on community structure that if they are removed from the ecosystem, there will be dramatic negative impacts.
Question 13 |
In which nutrient cycle does bacteria play a key role in the conversion of an essential organic compound from its atmospheric form to a form usable by organisms?
The water cycle | |
The carbon cycle | |
The nitrogen cycle | |
The phosphorus cycle |
Question 13 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). In the nitrogen cycle, nitrogen-fixing bacteria convert nitrogen gas (N2), which is not usable by plants, to a form that is usable by plants. These nitrogen-fixing bacteria reside in the root nodules of legumes.
Question 14 |
In the 1950s, scientists began observing a decline in the populations of certain bird species such as pelicans, ospreys and eagles. They found an accumulation of DDT in the tissues of the birds, which interfered with calcium deposits in their eggshells, rendering them weak. When the birds attempted to incubate their eggs, they cracked and the embryos died. DDT was applied to control insects in the 1940s.
What process describes how the DDT became toxic in the top predators of the ecosystem a decade after it was applied?
The greenhouse effect | |
The law of conservation of mass | |
Eutrophication | |
Biological magnification
|
Question 14 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Biological magnification is the process by which toxins accumulate, becoming more concentrated, as they move up the food chain.
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 14 questions to complete.
|
List |
Next Practice Test:
Competition & Cooperation >>
AP Biology Main Menu >>
