Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
Which property of water allows it to move upward from the roots of a tree to its leaves?
High specific heat | |
High heat of vaporization | |
Cohesion | |
Solvent of life |
Question 1 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). As water evaporates from the leaves of trees, the property of cohesion (attraction to another water molecule) allows the water molecules leaving the plant to pull molecules upward because they are attracted though hydrogen bonds.
Question 2 |
There are several emergent properties of water that contribute its powerful affect on living organisms. These emerging properties are mostly due to:
The abundance of water on Earth | |
The hydrogen bonds linking water molecules together | |
Water’s ability to moderate pH | |
The buffering ability of water |
Question 2 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The hydrogen bonds between water molecules are able to form, break and re-form frequently. Water’s life-sustaining properties are a result of hydrogen bonding that orders molecules into a higher level of structural organization.
Question 3 |
Which type of chemical bond involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in oppositely charged ions that are attracted to each other?
Covalent bond | |
Ionic bond | |
Hydrogen bond | |
Van der Waals interactions |
Question 3 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons, causing the atoms to have opposite charges and attract each other. Hydrogen bonds result from the attraction between partial positive and negative charges in atoms. Van der Waals interactions are weak attractions that occur when atoms and molecules are very close together.
Question 4 |
Which of the following molecules is a carbohydrate?
Palmitic acid | |
Collagen | |
Insulin | |
Lactose |
Question 4 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Anything that ends in the suffix –ose is a sugar and sugars are carbohydrates.
Question 5 |
Use the diagram below to answer questions 5–6.
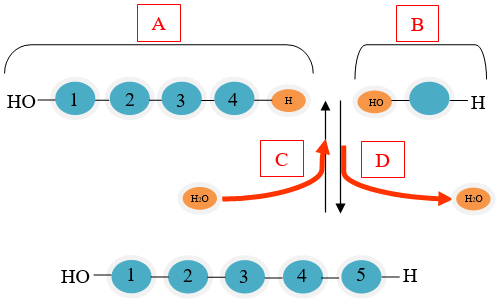
Which part of the diagram is showing a monomer?
A | |
B | |
C | |
D |
Question 5 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Monomers are small units that are joined together to form polymers.
Question 6 |

Which part of the diagram shows a condensation reaction?
A | |
B | |
C | |
D |
Question 6 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Condensation reactions occur when monomers are connected by the removal of a water molecule.
Question 7 |
There are four levels of protein structure. Which level includes the coils of the α helix and the folds of the β pleated sheets?
Primary structure | |
Secondary structure | |
Tertiary structure | |
Quaternary structure |
Question 7 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Primary structure refers to the sequence of amino acids. Secondary structure includes the α helix and the β pleated sheets. Tertiary structure is the overall shape of the protein. Quaternary structure consists of two or more polypeptide chains aggregated into a functional macromolecule.
Question 8 |
Which of the following statements correctly describes the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats?
Saturated fats tend to be solid at room temperature; unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature | |
Saturated fats are cannot pack together closely because of their bent structure; unsaturated fats can pack together because they are flat | |
Saturated fats come from plants and fish; unsaturated fats are from animals (except fish) | |
Saturated fats are considered “healthy” fats; unsaturated fats may contribute to cardiovascular disease |
Question 8 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Saturated fats tend to be solid at room temperature and are mostly obtained from animal, not plant, sources. Unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature and are primarily obtained from plants and fish sources. Healthful diets tend to be higher in unsaturated fats and lower in saturated fats.
Question 9 |
What determines the function of a protein?
The number of peptide bonds | |
The types of side chains | |
The protein’s specific structure | |
The tissue that produces the protein |
Question 9 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). The function of a protein depends on its ability to recognize and bind to some other molecule. For example, antibodies are specific to the invading virus or bacteria, and enzymes are specific to a substrate.
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 9 questions to complete.
|
List |
Next Practice Test:
Cell Structure & Function >>
AP Biology Main Menu >>
