Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
Which of the following nucleic acids is not found in RNA?
Cytosine | |
Thymine | |
Adenine | |
Guanine |
Question 1 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). In RNA, thymine (nucleic acid present in DNA) is replaced with uracil.
Question 2 |
Which is the correct sequence of information flow in a cell?
DNA → RNA → Protein | |
Protein → DNA → RNA | |
DNA → Protein → RNA | |
RNA → DNA → Protein |
Question 2 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Each gene on a DNA molecule directs the synthesis of a messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA molecule directs the production of a polypeptide.
Question 3 |
Which of the following is not a component of DNA?
Sugar | |
Phosphate | |
Nucleotide | |
Uracil |
Question 3 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Uracil is a RNA nucleotide.
Question 4 |
What aspect of the DNA molecule allows for it to replicate a duplicate copy of itself?
Base Pairing | |
Double helix structure | |
Origins of replication | |
Looped Domains |
Question 4 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The two strands of DNA are complimentary, which allows one strand to serve as a template for ordering nucleotides into a new, complimentary strand.
Question 5 |
What is the name of the DNA strand that elongates away from the replication fork in a series of segments?
Okazaki fragments | |
Lagging strand | |
Leading strand | |
Primer |
Question 5 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Since DNA is elongated in the 5' → 3' direction, only one strand can be elongated continuously. On the other strand, it must be replicated in segments since it can only be replicated in the 5' → 3', and this strand goes from 3' → 5'.
Question 6 |
DNA replication begins at short stretches of DNA with a specific sequence of nucleotides called:
Origins of replication | |
Template sequence | |
Replication fork | |
Replication bubble |
Question 6 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Origins of replication contain specific sequences of nucleotides where DNA replication begins.
Question 7 |
Which enzyme catalyzes the synthesis of new DNA by adding nucleotides to a preexisting chain?
DNA ligase | |
DNA polymerase | |
Helicase | |
Topoisomerase |
Question 7 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). DNA polymerase is responsible for adding nucleotides to a preexisting chain. DNA ligase joins together sugar-phosphate backbones of the Okazaki fragments into a continuous strand of DNA. Helicase unwinds parental double helix at replication forks. Topoisomerase breaks, swivels and rejoins DNA strands ahead of replication forks to relieve overwinding strain ahead of the replication forks.
Question 8 |
What property of DNA allows it to replicate and repair?
Specific base pairing | |
Double stranded structure | |
Antiparallel elongation | |
All of the above |
Question 8 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Specific base pairing, the double stranded structure and DNA’s antiparallel elongation are all important properties that contribute to DNA’s ability to replicate and repair.
Question 9 |
Which statement best describes the function promoter?
An enzyme that transcribes a new RNA chain by linking ribonucleotides to nucleotides on a DNA template. | |
A protein that prohibits gene transcription. | |
A nucleotide sequence in DNA that is the binding site of RNA polymerase, positioning the RNA polymerase to begin transcription at the appropriate position. | |
A sequence of nucleotides near the start of an operon where the active repressor can attach. |
Question 9 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). A promoter is a nucleotide sequence in DNA that is the binding site of RNA polymerase, positioning the RNA polymerase to begin transcription at the appropriate position.
Question 10 |
During this stage of gene expression, genetic information is copied from the template strand of DNA.
RNA Processing | |
Translation | |
Replication | |
Transcription |
Question 10 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Pre-messenger RNA carries information from DNA by copying the genetic information through a process called transcription.
Question 11 |
During this stage of gene expression, mRNA is processed through ribosomes and polypeptides are linked together into chains.
RNA Processing | |
Translation | |
Replication | |
Transcription |
Question 11 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). Molecules of mRNA are processed through ribosomes and codons are translated into amino acids. tRNA molecules translate the codons on the mRNA molecules, and deliver amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain.
Question 12 |
This process involves modifying the ends of the pre-mRNA molecules by modifying each end, cutting out introns and splicing remaining parts together.
RNA Processing | |
Translation | |
Replication | |
Transcription |
Question 12 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Enzymes change the ends of the pre-mRNA molecule by adding a 5' cap to the 5' end. The 3' end is modified by adding a poly-A tail. Also, during this stage, introns (non-coding segments of a nucleic acid) are removed and the remaining mRNA exons are joined back together.
Question 13 |
Which answer shows the correct sequence of information flow from gene to protein?
Transcription → Translation → RNA Processing | |
RNA Processing → Translation → Transcription | |
Transcription → RNA Processing → Translation | |
Translation → RNA Processing → Transcription |
Question 13 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Genetic information is transcribed onto a pre-mRNA molecule, then it is modified during RNA processing, and finally it is used to make polypeptides in translation.
Question 14 |
If a DNA template strand has the following sequence, what is the correct mRNA sequence?
DNA Template Strand Sequence: AAACCGAGTTTTGGCTCA | |
AAACCGAGT | |
UUUGGCUCA | |
GGGTTUGUA |
Question 14 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). mRNA’s pairs with DNA with the following base pairs: A – U and C – G.
Question 15 |
Questions 15–16
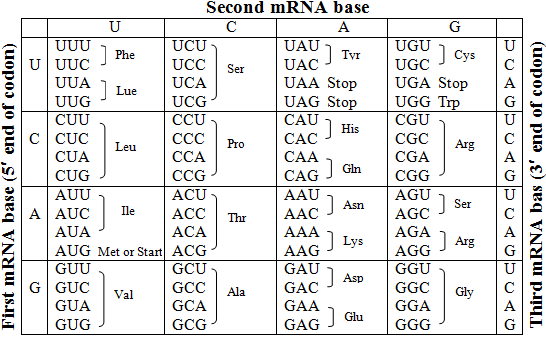
If a codon has the following sequence, what is the anticodon?
Codon: UCATCA | |
AGT | |
UCA | |
AGU |
Question 15 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). mRNA base’s complementary base pairs are A – U and C – G.
Question 16 |

If a DNA template strand’s DNA sequence is AAA, what amino acid will be formed?
Lys | |
Phe | |
Pro | |
Gly |
Question 16 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). A triplet code of AAA on a DNA strand is translated into the codon UUU. Using the chart, UUU codes for the amino acid Phe.
Question 17 |
Mad cow disease causes normal versions of a protein in the brain to misfold, causing brain damage. What is responsible for the change in the shape of the protein?
Repressor genes | |
RNA polymerase | |
Prions | |
The tryptophan operon |
Question 17 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Prions are misfolded versions of a protein which are infectious and cause brain diseases. Prion diseases occur when prion protein becomes abnormal and clump in the brain, When the prions accumulate in the brain it can cause memory impairment, personality changes, and difficulties with movement. Prion diseases are fatal.
Question 18 |
Which portion of the brain is responsible for homeostasis, transmission of information to and from higher brain centers, and coordinated movement? It is sometimes referred to as the “lower brain.”
Cerebellum | |
Cerebrum | |
Diencephalon | |
Brainstem |
Question 18 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The brainstem includes the midbrain, pons and medulla oblongata. The cerebellum coordinates movement and balance. The cerebrum is the information processing center of mammals. The diencephalon includes the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus.
Question 19 |
Which part of the cerebral cortex controls vision?
Frontal lobe | |
Temporal lobe | |
Parietal lobe | |
Occipital |
Question 19 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The frontal lobe controls speech. The temporal lobe controls smell and hearing. The parietal lobe controls speech, taste, and reading. The occipital lobe controls vision.
Question 20 |
If your grandfather started showing symptoms of muscle tremors, poor balance, and shuffling gait, which of the following diseases should you suspect?
Alzheimer’s Disease | |
Parkinson’s Disease | |
Schizophrenia | |
Depression |
Question 20 Explanation:
The correct answer is (B). The question describes symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease, a neurodegenerative disorder that comes about as a result of the loss of dopamine-producing neurons.
Question 21 |
If an individual suspected of having brain damage presented symptoms affecting his verbal and written communication, the damage is likely to be present in which lobe(s)?
Temporal lobe | |
Occipital lobe | |
Temporal and Frontal lobes | |
Frontal and Parietal lobes |
Question 21 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The frontal and parietal areas of the brain are associated with speech and reading.
Question 22 |
In the fall of 1957, Hans Fromme was conducting research at the Frankfurt Zoological Institute in Germany. He noticed that several caged European robins were becoming restless and attempting to fly to the southwestern part of the cage. Fromme wondered how the birds knew which direction they were supposed to be migrating, since they were in a darkened room and could not see any landmarks, the sun or the stars.
Which type of sensory cell receptor is responsible for guiding the migration of the robins?
Mechanoreceptors | |
Chemoreceptors | |
Electromagnetic receptors | |
Thermoreceptors |
Question 22 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Electromagnetic receptors detect electromagnetic energy and assist animals as they migrate along the Earth’s magnetic field lines.
Question 23 |
Which type of signaling molecule is triggered by endocrine glands?
Hormones | |
Local regulators | |
Neurotransmitters | |
Pheromones |
Question 23 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Hormones are secreted into extracellular fluids by endocrine cells, and reach their target cells through the bloodstream.
Question 24 |
Which of the following correctly describes aspects of the endocrine system and the nervous system?
Both systems act very quickly to relay information to various parts of the body | |
Both systems send impulses directly to a specific part of the body as an impulse that targets specific cells | |
In both systems information can be received by various cells in different organs and in different parts of the body | |
Both systems contribute to maintaining a stable internal environment within an organism |
Question 24 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). The endocrine system uses hormones released into the bloodstream that travel to all parts of the body. Hormones are slow acting and can affect various cells. The nervous system uses impulses to quickly send information along axon to a specific location. Both systems help maintain homeostasis.
Question 25 |
Which of the following gland is incorrectly matched to its function?
Thyroid – involved in biological rhythms | |
Pancreas – raises and lowers blood glucose levels | |
Adrenal glands – secrete hormones in response to stress | |
Pineal gland – involved in the regulation of sleep patterns |
Question 25 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The thyroid gland stimulates and maintains metabolic processes and lowers blood calcium levels. The pancreas raises and lowers blood glucose levels. The adrenal glands raise blood glucose levels, increase metabolic activities, constrict certain blood vessels and promote reabsorption of sodium and excretion of potassium in the kidneys. The pineal gland is involved in biological rhythms.
Question 26 |
Chromosome structure can be altered by damages to the chromosome, or during an error in meiosis.
When a chromosomal fragment reattaches to the original chromosome in reverse order, it is called:An inversion | |
A translocation | |
A deletion | |
A duplication |
Question 26 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). A deletion occurs when a chromosome fragment is lost. A duplication leads to the addition of one or copies of a preexisting DNA sequence to a chromosome. A translocation is the result of a chromosomal breakage during which the fragment of one chromosome joins a nonhomologous chromosome resulting in a rearrangement of DNA.
Question 27 |
If a mutation causes a misplacement of a structure on an organism, such as a leg growing where an antennae on a fruit fly should be, the mutation is likely to be in:
A homeotic genes | |
ras genes | |
p53 genes | |
Maternal effect genes |
Question 27 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Homeotic genes control the development of the overall organization of the body.
Question 28 |
If a mutation in a cell inhibits the production of a tumor-suppressor protein, the cell is much more likely to:
Develop cancer | |
Enter homeostasis | |
Enter apoptosis | |
Become an embryonic lethal |
Question 28 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Cells contain genes that inhibit cell division, called tumor-suppressor genes, which help to prevent uncontrolled cell growth, or cancer.
Question 29 |
What type of point mutation causes translation to be terminated prematurely, resulting in a shorter polypeptide than was encoded by the normal gene?
Nonsense mutation | |
Missense mutation | |
Frameshift mutation | |
Deletion |
Question 29 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). Typically substitutions result in missense mutations, and the altered codon still codes for an amino acid. But if a point mutation changes a codon for an amino acid to a stop codon, it is called a nonsense mutation.
Question 30 |
This type of mutation frequently alters the genetic message by changing the reading frame, causing all the nucleotides “downstream” of the mutation to be improperly grouped into codons.
Mutagen | |
Base-pair substitution | |
Nonsense mutation | |
Frameshift mutation |
Question 30 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). If a nucleotide is inserted or deleted in a gene, it will change the reading frame of the genetic message. The triplet grouping of bases on the mRNA that is read during translation will be altered, along with every grouping after the insertion or deletion. The result is typically extensive missense.
Question 31 |
What enzyme is responsible for the reverse information flow of RNA to DNA in retroviruses, such as HIV, allowing the virus’s genetic information to be permanently integrated into the hosts cell’s DNA?
DNA polymerase | |
RNA polymerase | |
Reverse transcriptase | |
Telomerase |
Question 31 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Reverse transcriptase catalyzes the formation of a strand of DNA from an RNA template.
Question 32 |
Questions 32–33
In the classic experiment by Frederick Griffith, two strains of the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae were studied. The smooth “S” strain bacteria can cause pneumonia in mice because they have a capsule that protects them from the defense system of animals. The rough “R” strain bacteria do not have a capsule, and are thus nonpathogenic. Griffith injected the mice with two strains of the
bacteria to test for the trait of pathogenicity.
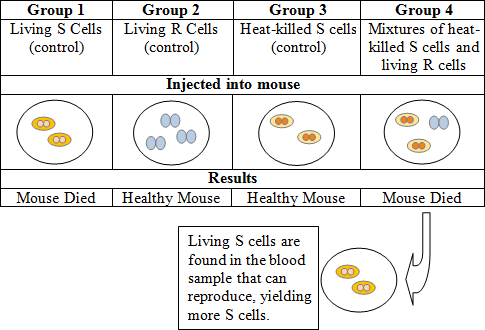

What important conclusion did Griffith reach after conducting his experiment?
Killing bacteria cells with heat is not an effective way to cure pneumonia | |
Heat-killed S cells regenerate themselves inside of organisms | |
It is impossible to kill Streptococcus pneumonia | |
Living R bacteria had been changed into pathogenic S bacteria by an unknown substance |
Question 32 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Griffith was attempting to develop a vaccine against pneumonia when he discovered the process of transformation, which is a change in genotype and phenotype due to the assimilation of external DNA by a cell.
Question 33 |
In the classic experiment by Frederick Griffith, two strains of the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae were studied. The smooth “S” strain bacteria can cause pneumonia in mice because they have a capsule that protects them from the defense system of animals. The rough “R” strain bacteria do not have a capsule, and are thus nonpathogenic. Griffith injected the mice with two strains of the
bacteria to test for the trait of pathogenicity.


Which group demonstrates that DNA is the agent of transformation?
Group 1 | |
Group 2 | |
Group 3 | |
Group 4 |
Question 33 Explanation:
The correct answer is (D). Since it was found that the S cells were able to reproduce, the agent of transformation must be DNA.
Question 34 |
Which type of bacteriophage reproduces only by the lytic cycle?
Virulent phage | |
Temperate phage | |
Prophage | |
Lysogenic phage |
Question 34 Explanation:
The correct answer is (A). The lytic cycle is the type of phage reproductive cycle that results in the death of the host cell. The bacterium breaks open (lyses) and releases the phages that were produced within the cell.
Question 35 |
Bacteriophages are able to carry bacterial genes from one host cell to another resulting in genetic recombination. This process is called:
Conjugation | |
Transformation | |
Transduction | |
Mutation |
Question 35 Explanation:
The correct answer is (C). Transduction occurs when bacteriophages carry bacterial genes form one host cell to another. This usually results from an accident during the phage reproductive cycle. The virus that carries the DNA may not be able to reproduce because it lacks its own genetic information. The virus may be able to attach to another bacterial cell and inject the bacterial DNA into the next cell. If this DNA replaces the homologous region of the recipient cell’s chromosomes by DNA recombination, then it has introduced genetic variation into the subsequent cell.
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 35 questions to complete.
|
List |
Next Practice Test:
Natural Selection >>
AP Biology Main Menu >>
